Image Classification
Task: assigning an input image one label from a fixed set of categories
Images are defined as tensors of integers between [0,255], e.g. 800 x 600 x 3
Challenges:
- Viewpoint variation
- Scale variation
- Deformation
- Occlusion
- Illumination conditions
- Background clutter
- Intra-class variation
A good image classification model must be invariant to the cross product of all these variations, while simultaneously retaining sensitivity to the inter-class variations.
The data-driven approach: first accumulating a training dataset of labeled images, then develop learning algorithms to learn about them.
The image classification pipeline:
- Input: Input a set of N images, each labeled with one of K different classes.
- Learn: use the training set to learn what every one of the classes looks like. training a classifier, or learning a model.
- Evaluate: evaluate the quality of the classifier by asking it to predict labels for a new set of images that it has never seen before.
Nearest Neighbor Classifier
Here is the English translation of your content.
L1 Distance (Manhattan Distance)
L1 Distance is the sum of the absolute values of the differences between corresponding dimensions of two vectors. The calculation formula is:
L2 Distance (Euclidean Distance)
L2 Distance is the square root of the sum of the squared differences between corresponding dimensions of two vectors. This is what we commonly refer to as the straight-line distance between two points. The calculation formula is:
Note on L2: Squaring amplifies values, thereby magnifying the influence of outliers.
Evaluation
For evaluation, we use accuracy, which measures the fraction of predictions that were correct.
k-Nearest Neighbr Classifier
The idea: we will find the top k closest images, and have them vote on the label of the test image.
Hyperparameters
It’s often not obvious what values/settings one should choose for hyperparameters.
We cannot use the test set for the purpose of tweaking hyperparameters.
-> Split your training set into training set and a validation set. Use validation set to tune all hyperparameters. At the end run a single time on the test set and report performance.
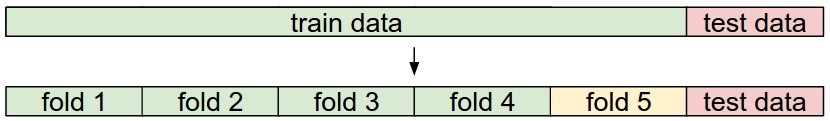
Cross-validation
Cross-validation: iterating over different validation sets and averaging the performance across these.